Building a Globally Distributed, High-Performance Application with Azure Cosmos DB
Building a Globally Distributed, High-Performance Application with Azure Cosmos DB
Meta Description: Learn how to design and implement a globally distributed, high-performance application using Azure Cosmos DB. This guide covers architecture, configuration, best practices, and advanced troubleshooting for enterprise-grade solutions.
Introduction
In today's digital era, the need for globally distributed, high-performance applications is more critical than ever. As a Senior Cloud Architect, I have seen firsthand how Azure Cosmos DB can be a game-changer for such applications. Azure Cosmos DB is a fully managed, globally distributed NoSQL database service designed to provide low-latency, high-availability, and scalability for modern applications. This blog post will guide you through the strategic importance, architecture, configuration, and best practices for building a high-performance application using Azure Cosmos DB.
Technical Architecture Overview
Azure Cosmos DB is a multi-model database service that supports document, key-value, graph, and column-family data models. It offers turnkey global distribution, which means you can distribute your data to any number of Azure regions worldwide with a single click. The service automatically handles data replication and provides a 99.999% availability SLA for multi-region accounts.
To make the most of Azure Cosmos DB, it's important to understand its core components:
Database Account: The top-level resource that contains databases and defines the regions where your data is replicated.
Database: A logical container for a set of containers (similar to a namespace).
Container: A schema-agnostic container for items (documents, rows, nodes, or edges).
Item: The content stored within a container (e.g., a JSON document).
For a globally distributed application, Azure Cosmos DB provides several consistency models (from strong to eventual) to balance between consistency, availability, and latency. The five consistency levels are:
Strong
Bounded staleness
Session
Consistent prefix
Eventual
Choosing the right consistency level is crucial for your application's performance and user experience.
Implementation Architecture
To illustrate a real-world deployment, let’s consider a scenario where we need a globally distributed e-commerce application that requires low-latency access for users across North America, Europe, and Asia. The goal is to ensure that users experience fast response times regardless of their geographic location.
Here’s a high-level architecture for such an application:
Frontend: A web application hosted on Azure App Service or Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) deployed in multiple regions.
Backend Services: Microservices hosted on Azure Functions or Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) that interact with Azure Cosmos DB.
Azure Cosmos DB: A globally distributed database account with read and write regions in North America (e.g., East US), Europe (e.g., West Europe), and Asia (e.g., Southeast Asia).
Azure Traffic Manager: To route user requests to the nearest App Service or AKS instance based on geographic location.
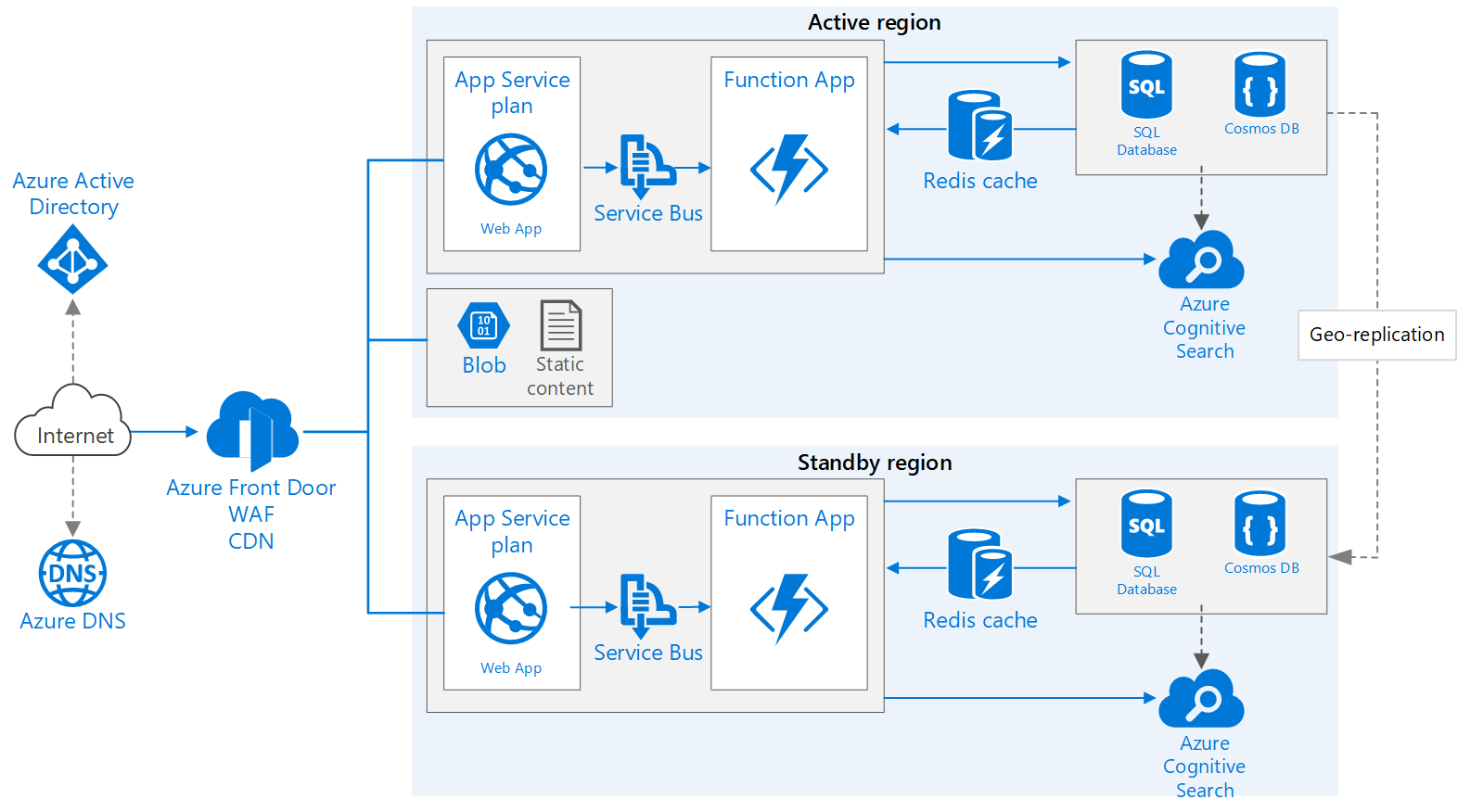
Configuration Walkthrough
Let’s walk through the steps to set up a globally distributed Azure Cosmos DB account and configure it for a high-performance application.
Step 1: Create an Azure Cosmos DB Account
Log in to the Azure portal.
Click on "Create a resource" and search for "Azure Cosmos DB."
Click "Create" and fill in the required details such as subscription, resource group, account name, API (e.g., Core (SQL)), and location (primary region).
Click "Review + create" and then "Create" to provision the account.
Step 2: Enable Global Distribution
Once the account is created, navigate to the "Replicate data globally" section in the Azure Cosmos DB account settings.
Add additional regions where you want to replicate your data (e.g., West Europe and Southeast Asia).
Configure the "Multi-region writes" option if you need write capabilities in multiple regions.
Step 3: Create a Database and Container
Within your Azure Cosmos DB account, navigate to the "Data Explorer" tab.
Click on "New Container" and provide a database ID (create a new one if necessary), container ID, partition key, and throughput (e.g., 400 RU/s).
Click "OK" to create the container.
Step 4: Configure Consistency Level
Navigate to the "Default Consistency" section in the Azure Cosmos DB account settings.
Choose a consistency level that fits your application’s needs (e.g., "Session" for a balance between consistency and performance).
Step 5: Connect Your Application to Azure Cosmos DB
Retrieve the connection string or primary key from the "Keys" section of your Azure Cosmos DB account.
Use the Azure Cosmos DB SDK (available for .NET, Java, Python, Node.js, etc.) to connect your application to the database.
Implement retry policies and handle transient faults using the SDK’s built-in retry mechanisms.
Troubleshooting & Monitoring
Monitoring and troubleshooting are crucial for maintaining a high-performance application. Azure Cosmos DB provides several tools for this purpose:
Azure Monitor: Use Azure Monitor to collect and analyze metrics such as request units (RUs), latency, and error rates.
Diagnostic Logs: Enable diagnostic logs to capture detailed information about operations and errors.
Azure Cosmos DB Insights: A pre-built workbook in Azure Monitor that provides a comprehensive view of your Cosmos DB account’s performance.
Query Performance: Use the "Query Metrics" feature in the Data Explorer to analyze the performance of your queries and identify potential optimizations.
Common issues and their solutions include:
High RU Consumption: Optimize queries, use indexing policies, and consider increasing throughput if necessary.
Latency Issues: Ensure that your application is connecting to the nearest region and that your data is distributed appropriately.
Partition Key Issues: Choose a partition key that distributes data evenly to avoid "hot" partitions.
Enterprise Best Practices 🚀
To ensure a robust and secure implementation, follow these best practices:
Security-First Design: Use Azure Active Directory (AAD) for authentication and role-based access control (RBAC) to manage permissions.
Automated Backups and Disaster Recovery: Azure Cosmos DB automatically backs up your data every 4 hours and retains the last two backups. However, for additional safety, you can also use Azure Backup for Cosmos DB.
Cost Management: Monitor and optimize your RU consumption to manage costs effectively. Use serverless or autoscale throughput for variable workloads.
Data Modeling: Design your data model to make the most of Cosmos DB’s capabilities. Normalize or denormalize data based on your query patterns.
Indexing Policies: Customize indexing policies to include only the necessary paths and exclude others to save on storage and RU costs.
Conclusion
Building a globally distributed, high-performance application with Azure Cosmos DB requires a strategic approach to architecture, configuration, and best practices. By leveraging Azure Cosmos DB’s turnkey global distribution, multiple consistency models, and robust monitoring tools, you can create an application that provides a seamless and responsive experience for users worldwide. As a Senior Cloud Architect, I highly recommend Azure Cosmos DB for any application that demands high availability, low latency, and global scalability. By following the steps and best practices outlined in this post, you can ensure a successful and efficient implementation.
For further reading, check out the Azure Cosmos DB documentation and the Azure Architecture Center for more in-depth guidance on designing distributed applications.
By following this structured, in-depth guide, you should be well on your way to building a high-performance, globally distributed application with Azure Cosmos DB. Happy coding! 🚀




Comments
Post a Comment
Thank You for Sharing your feedback, We hope article was helpful in some way to you.